Our R9 Class Treaty
- bags under your desk
- no food or drink
- no running
- dont touch experiment
- report any breakages or spills
- do not taste or sniff anything
Safety in a laboratory.
teacher shoes practical teacher laboratory ask sniff teacher breakages
- Follow the instructions given to you by the teacher.
- You must not enter the laboratory without your teacher.
- Report all breakages to your teacher.
- You must never eat or drink in a laboratory
- shoes must be worn at all times.
- If you spill something you should tell your teacher immediately.
- You should wash your hands after every practical activity.
- You should know what you are doing. If in doubt ask your teacher.
- Never taste or sniff chemicals.
In your group, discuss how the following scenarios could be dangerous.
- Not putting your bag under your desk.
- Running around in the laboratory.
- Not wearing shoes in a laboratory.
- Shaking a test tube with your thumb over its mouth?
How do we work in this laboratory?
- Beginning and End of class: Lining up, Entry, Seating,
- Equipment tray: equipment list and details.
- Test tube - This is used for experiments using liquids.They have a bung that can be placed in the top. Test tubes sit in a test tube rack.
- Conical Flask - This is used for experiments with liquid up to 150 ml. The flask has a rubber bung for the top and the glass is heat proof.
- Glass Stirring rod - This is a 20cm glass rod used to stir and mix any liquids together.
- Test tube tongs - These are used to hold a hot test tube after an experiment.
- Spatula - This is for holding very small amounts of chemical powders.
- Funnel - used to channel liquids into a smaller container.
- Measuring Cylinder - This is used to measure liquids for experiments. The liquids will be poured into a beaker or test tube once measured out.
S
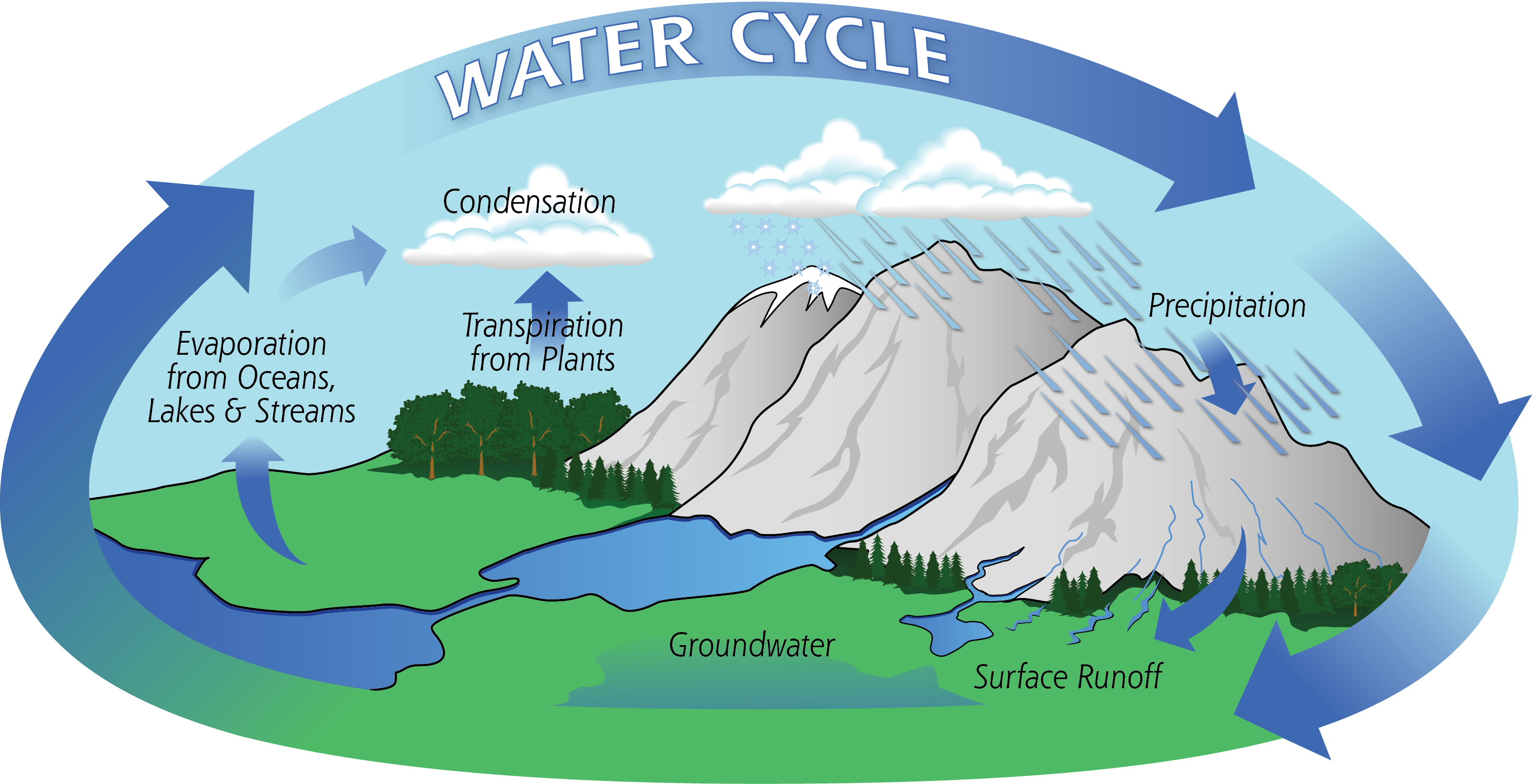
Hurumanu: The Water Cycle
AIM: TO LEARN ABOUT WATER ON EARTH.
Definition:
Scientific words:
- Evaporation. When water is heated by radiant energy it turns into water vapor.
- Transpiration. Evaporation from plants.
- Condensation. When water vapor cools, molecules join together and form clouds.
- Precipitation. When clouds get heavy the waters falls as rain, sleet, hail, or snow.
- Acidification: the action or process of making or becoming acidic.
THE WATER CYCLE SONG
THE WATER CYCLE EXPERIMENT
Bag 1: Normal Water cycleBag 2: Water cycle with CO2 added: like Oceans in climate changeBag 3: Water cycle with ice added: like Antarctica in climate changeMaterial:
Steps:
Two Images:
Findings:
The Water CycleAcid Water CycleDoes it cycle?2 3 Amount of Water2 3 Acidity3 1 Key: Water and acidity amount: 0 = none1 = small2 = largeOther comments:
Conclusion:
My Investigation on climate changeACIDIFICATION the ocean become more wasted
DEFINITION: its a big wide area when trees gets cut of
What is happening to the oceans? The ocean contains about 97% of all the water on Earth. The ocean plays a starring role in whatever happens with the environment. One big part of its role is to soak up energy (heat) and distribute it more evenly around the EarthWhat does this do to shellfish?HOW DOES CLIMATE CHANGE CONTRIBUTE TO THE ACIDIFICATION OF OUR OCEANS?

No comments:
Post a Comment